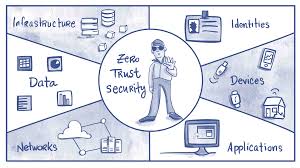
What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no one inside or outside your network is trustworthy by default. Instead of relying on perimeter-based defenses, Zero Trust continuously verifies every user, device, and application trying to access your systems — even if they’re already inside the network.
Key Principle:
“Never trust, always verify.”
Why Zero Trust Is Important for SMBs
| Reason | Impact for SMBs |
|---|---|
| Remote Work | Employees work from various locations/devices — perimeter security is obsolete |
| Cloud Services Usage | SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS apps require tighter access control and identity validation |
| Ransomware & Phishing Attacks | SMBs are common targets due to weaker defenses |
| Compliance Requirements | GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS increasingly favor Zero Trust approaches |
| Supply Chain Risks | Even one compromised vendor can affect your entire business |
Core Pillars of Zero Trust Architecture
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
-
Verify every user and role
-
Enforce strong authentication (MFA)
-
-
Device Security
-
Authenticate and validate device posture
-
Block access from compromised or unknown devices
-
-
Network Segmentation
-
Limit lateral movement with micro-segmentation
-
-
Least Privilege Access
-
Give users the minimum access required to do their jobs
-
-
Continuous Monitoring
-
Audit all access and monitor behavior anomalies
-
-
Encryption & Secure Communication
-
Encrypt all data in transit and at rest

zero trust security architecture for SMBs
-
How SMBs Can Implement Zero Trust (Step-by-Step)
1. Assess Your Current Environment
-
Inventory users, devices, applications, data flows
-
Identify critical systems and crown jewels (e.g., financials, customer PII)
2. Implement Identity & Access Controls
-
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users
-
Use Single Sign-On (SSO) with role-based access control (RBAC)
✅ Recommended Tools:
3. Strengthen Endpoint Security
-
Ensure all endpoints (laptops, mobiles, POS devices) have:
-
Antivirus/EDR
-
Full disk encryption
-
Remote wipe capability
-
✅ Tools:
4. Segment Your Network
-
Create network zones for HR, finance, guest Wi-Fi, etc.
-
Use firewalls and VLANs to restrict lateral movement
✅ Tools:
-
Ubiquiti UniFi for SMB networking
-
Cisco Meraki for cloud-managed segmentation
5. Limit Application Access
-
Implement Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) instead of VPN
-
Restrict access to apps based on user/device identity
✅ Tools:
6. Encrypt and Monitor Data
-
Enable TLS 1.3 across your website and services
-
Encrypt backups and cloud storage
-
Use Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies
✅ Tools:
7. Implement Continuous Monitoring
-
Use a lightweight SIEM to log and analyze activity
-
Set alerts for unusual logins, access patterns
✅ Tools:
Example: Zero Trust in a Small E-Commerce Business
| Component | Traditional Approach | Zero Trust Upgrade |
|---|---|---|
| User Logins | Username/password only | MFA + SSO with Okta or Google Workspace |
| Remote Work Access | VPN access to all servers | ZTNA with Cloudflare Access |
| Internal Network | Flat LAN | VLAN segmentation (POS, staff, guest Wi-Fi separated) |
| Endpoint Protection | Basic antivirus | EDR + device health checks (SentinelOne) |
| File Access | Open shared drives | Role-based access + cloud DLP (Microsoft Purview) |
Best Practices for Zero Trust Success in SMBs
-
Start Small, Scale Smart
-
Begin with MFA, then expand to ZTNA and segmentation
-
-
Prioritize High-Value Targets
-
Protect customer data and financial systems first
-
-
Leverage Managed Security Providers
-
Use MSSPs if you lack in-house security expertise
-
-
Train Employees
-
Run phishing simulations and cybersecurity awareness campaigns
-
-
Automate Where Possible
-
Use automated alerts, access reviews, and patch management
-
ROI of Zero Trust for SMBs
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Reduced Risk | Stops breaches early and limits attack spread |
| 💰 Lower Cost of Recovery | Faster detection → fewer losses from downtime/data |
| 📈 Improved Trust | Customers and partners view you as a secure vendor |
| 🧾 Regulatory Compliance | Simplifies HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR audit readiness |
Additional Resources

Conclusion
Zero Trust is not just for large enterprises. With today’s cloud-native tools and simplified architectures, even small and mid-sized businesses can deploy Zero Trust in affordable, incremental steps. Start with user identity and MFA, secure endpoints, segment your network, and adopt ZTNA — all within reach for modern SMBs.